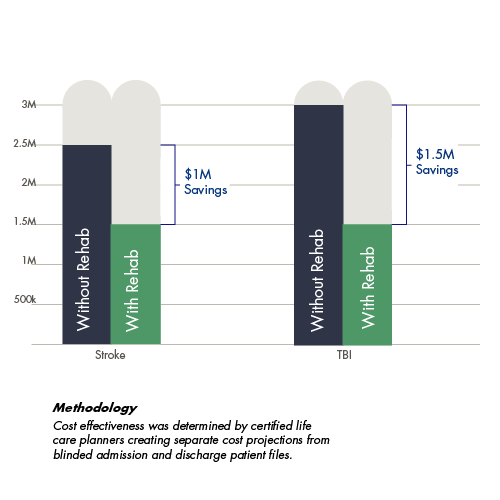
In today’s healthcare climate, Increasing the quality of care while reducing costs is a constant imperative. With every therapy we offer and every patient we admit, CNS strives to optimize treatment and minimize costs. Patient data reveals that CNS achieves both objectives. Intensive therapy produces a more durable outcome, which in turn reduces future healthcare costs, such as rehospitalization. For payors, families, and patients, the long-term rehabilitation value enhances quality of life post injury and impacts return on investment. CNS outcomes are noted here to inform and guide consumers.

Payors, Patients and Families
N=922 Participants
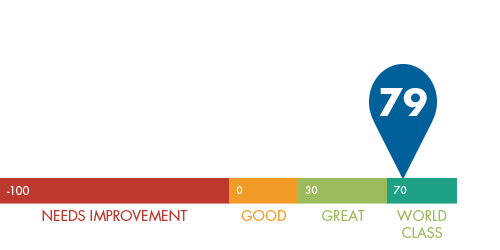
"Would you recommend CNS to friends of family?"
N=922 Participants
In a groundbreaking study, CNS outcome data in key areas of rehabilitation delivery was gathered and analyzed by a third-party consultant and consisted of 15 million healthcare claims (covering more than 1 million individuals) over a 5-year period. The consultant is not affiliated with the Centre for Neuro Skills.
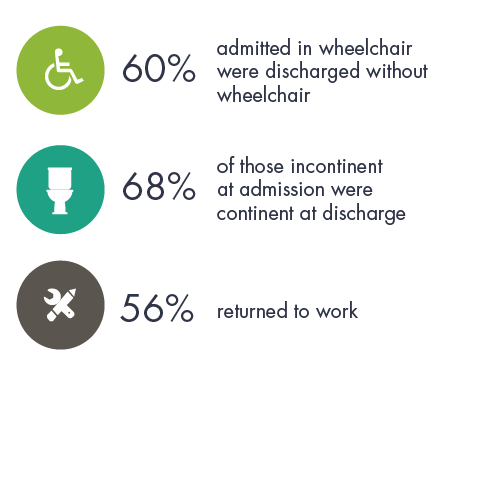
Metrics included maximizing treatment, comparing healthcare costs, measuring performance, tracking rehospitalization rates, medication savings, and customer satisfaction scores.
In key areas of rehabilitation for traumatic brain injury and stroke, CNS data reflects an impressive mastery of multidisciplinary care. CNS has focused on outcome-driven solutions since its inception in 1980. The Executive Summary published metrics that substantiate this legacy of innovation.
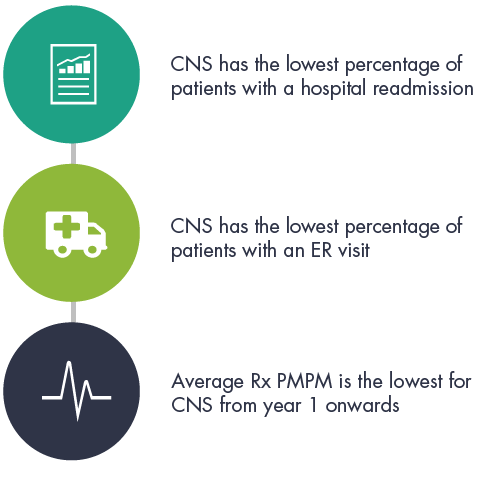
Among patients with over $100,000 in therapy costs.
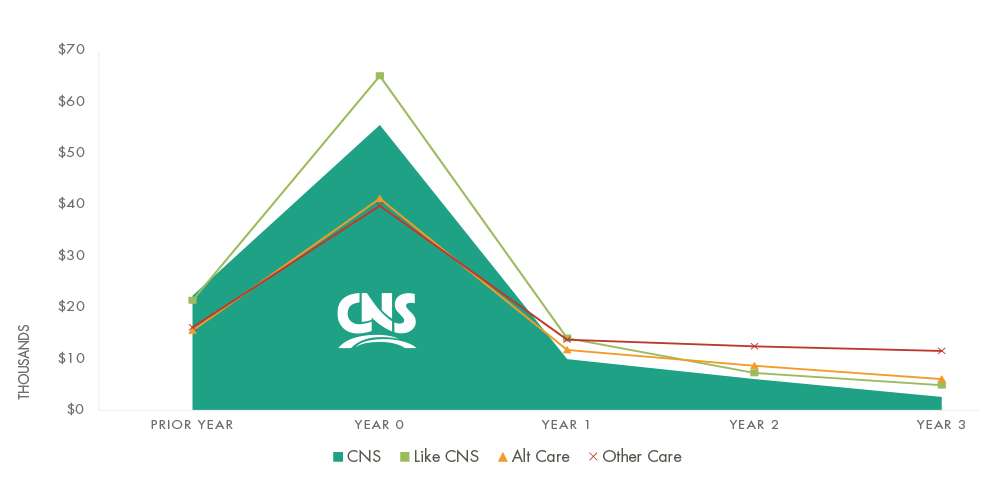 CNS Is More Efficient Throughout the Stages of Care
CNS Is More Efficient Throughout the Stages of Care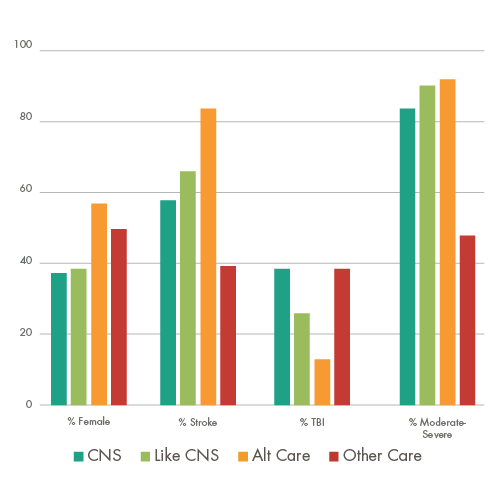
To establish a baseline comparison with other rehabilitation providers, 15 million brain injury claims were reviewed to identify patient journey value analytics
CNS patients had the highest monthly cost indicating more medically complex patients at the time of injury and admission to CNS.
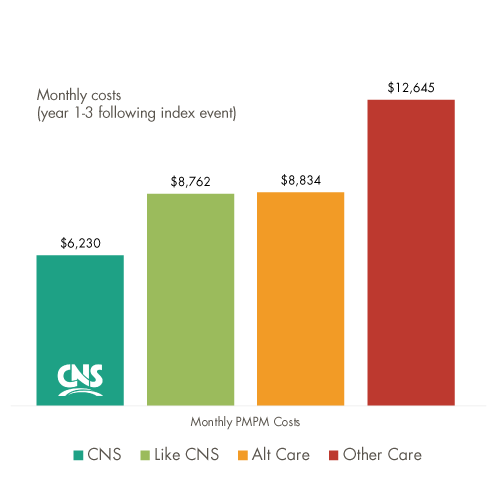
CNS patients exhibited the most substantial decline in monthly cost of all patient journeys. By year 3, CNS patient monthly cost was 30% lower than Like-CNS.
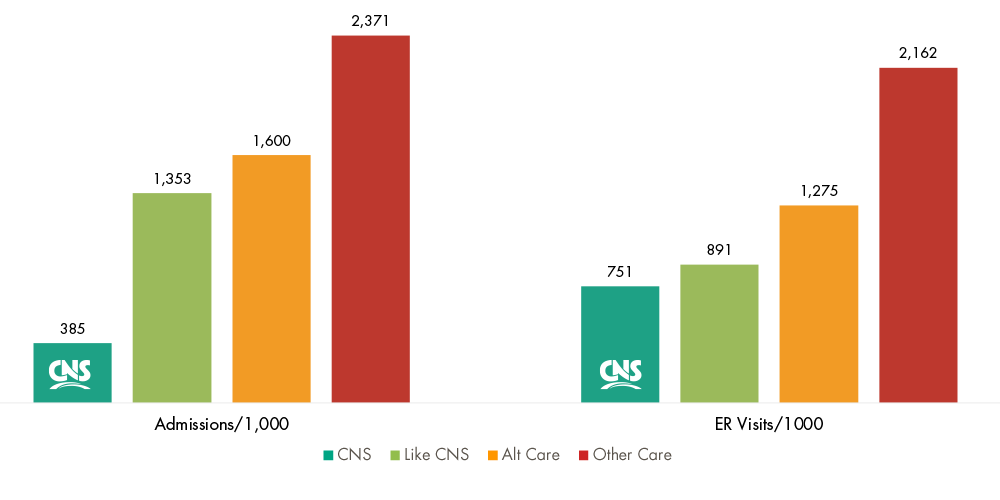
CNS inpatients had 67% less claims with inpatient admissions and 14% less emergency room visits than Like-CNS facilities.
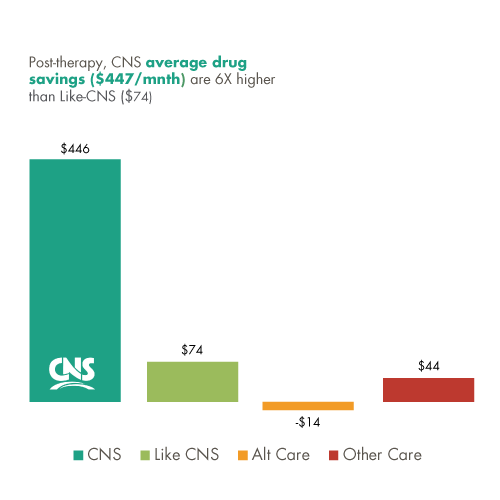
CNS patients’ prescription drug costs were the lowest of all patient journey models beginning the first year after the index-event.