Brain Injury Overview
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) can significantly affect many cognitive, physical, and psychological skills. Physical deficit can include ambulation, balance, coordination, fine motor skills, strength, and endurance. Cognitive deficits of language and communication, information processing, memory, and perceptual skills are common. Psychological status is also often altered. Adjustment to disability issues are frequently encountered by people with TBI.
Brain injury can occur in many ways. Traumatic brain injuries typically result from accidents in which the head strikes an object. This is the most common type of traumatic brain injury. However, other brain injuries, such as those caused by insufficient oxygen, poisoning, or infection, can cause similar deficits.
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) is characterized by one or more of the following symptoms: a brief loss of consciousness, loss of memory immediately before or after the injury, any alteration in mental state at the time of the accident, or focal neurological deficits. In many MTBI cases, the person seems fine on the surface, yet continues to endure chronic functional problems. Some people suffer long-term effects of MTBI, known as postconcussion syndrome (PCS). Persons suffering from PCS can experience significant changes in cognition and personality.
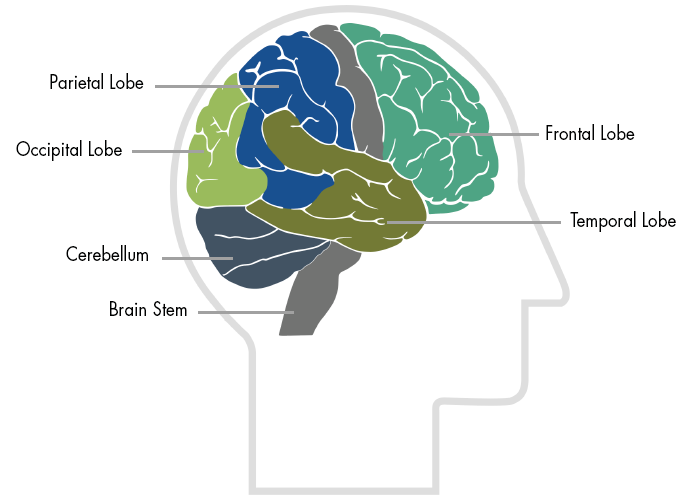
Most traumatic brain injuries result in widespread damage to the brain because the brain ricochets inside the skull during the impact of an accident. Diffuse axonal injury occurs when the nerve cells are torn from one another. Localized damage also occurs when the brain bounces against the skull. The brain stem, frontal lobe, and temporal lobes are particularly vulnerable to this because of their location near bony protrusions.
The brain stem is located at the base of the brain. Aside from regulating basic arousal and regulatory functions, the brain stem is involved in attention and short-term memory. Trauma to this area can lead to disorientation, frustration, and anger. The limbic system, higher up in the brain than the brain stem, helps regulate emotions. Connected to the limbic system are the temporal lobes which are involved in many cognitive skills such as memory and language. Damage to the temporal lobes, or seizures in this area, have been associated with a number of behavioral disorders. The frontal lobe is almost always injured due to its large size and its location near the front of the cranium. The frontal lobe is involved in many cognitive functions and is considered our emotional and personality control center. Damage to this area can result in decreased judgement and increased impulsivity.
Conditions and Other Information
- anoxia and hypoxia
- aphasia
- biomechanics of brain injury
- cognitive and communication disorders
- coma
- concussion
- cure for brain injury
- epidemiology of traumatic brain injury
- sexual dysfunction
- traumatic brain injury recovery
- traumatic brain injury statistics
- what is the prognosis for traumatic brain injury
- vision problems

